Indigoid Dyes
by : --
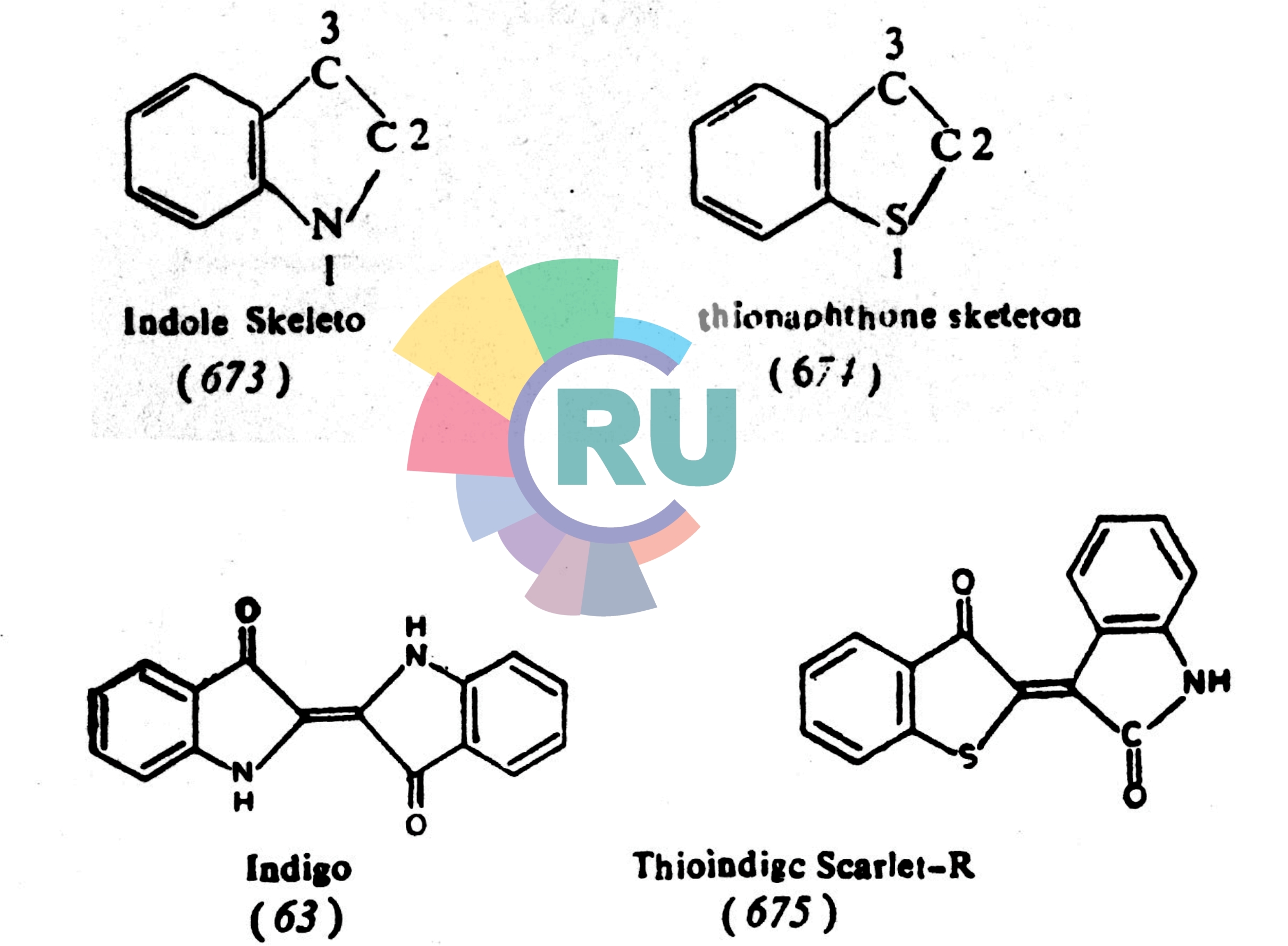
Indigoid dyes contain —CO—CH=CH—CO— basic structure responsible for vatting and include thioindigoid dyes. Depending upon the positions of attachment of two ring skeletons and having both idole (673) systems, one indole (673) and one thionaphthene (674) systems or both thionaphthene (674) systems, the idigoid dyes are classified. For the simplicity, the entire classification is not given here however, two examples and belonging to 2,2—bis—indole indigos, viz; indigo (63) and another belonging to 2—thionaphthene—3'—indole indigos, viz; thioindingo scarlet R (675) are given to understand how they are classified.
Indigo (63) can be prepared by following various synthetic routes. The first route is to condense anthranilic acid (78) with chloroacetic acid, the resultant intermediate phenylglycineorthocarboxylic acid is cyclised by fusing with alkali to get indoxyl which is air oxidised in alkaline medium to get the dye (63). The reaction is already described under the use of chloroacetic acid, an aliphatic intermediate for dyes.
